What is Chiropractic?
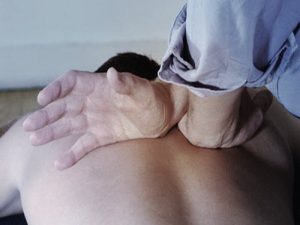 Chiropractic is a branch of the healing arts that predominately focuses on clinical conditions involving the spine, specifically the low back, mid-back and neck. It is a conservative, drug-free, non-invasive, hands-on approach to healing that emphasizes the importance of the structure and function of the human body.
Chiropractic is a branch of the healing arts that predominately focuses on clinical conditions involving the spine, specifically the low back, mid-back and neck. It is a conservative, drug-free, non-invasive, hands-on approach to healing that emphasizes the importance of the structure and function of the human body.
Chiropractic is a regulated profession in all Canadian jurisdictions with a broad scope of practice, as defined by legislation. Chiropractors are entitled to diagnose and treat a wide variety of clinical conditions, and are also permitted to provide preventive care and offer healthful lifestyle recommendations.
How does a person become a Chiropractor? What are their qualification and education?
In order to apply to an accredited chiropractic college, a person must have successfully completed 4 years of undergraduate education and obtained a Bachelors degree from an accredited university. Of the roughly 600 eligible students who apply annually to the Canadian Memorial Chiropractic College (CMCC- the only English speaking college in Canada), only 200 are granted admission, and only 180 or so graduate a year.
The 4-year chiropractic program, consisting of 50 courses, is very similar to a conventional medical program. Students are taught courses in anatomy, histology, embryology, physiology, microbiology, pathology and clinical diagnosis. However, where medical students are primarily taught to manage patient’s problems using drugs or surgery, chiropractic students are taught to use a multitude of hands-on techniques. This training is extensive. The last year at the chiropractic clinic is an internship, where students are permitted to treat patients under the direct supervision of a licensed chiropractor.
Upon graduation, a student must still successfully pass both provincial and national exams before they can become licensed to practice chiropractic in Canada. As a chiropractor, each provincial licensing body has a number of statutory regulations, standards of practice, policies and guidelines a practitioner must adhere to, including specific continuing education requirements, in order to maintain their license.
What Conditions do Chiropractors Most Commonly Treat?
Low back pain, neck pain and headaches comprise roughly two-thirds of what chiropractors treat. Low back and neck pain are often accompanied by numbing and tingling in the legs and arms, respectively; these conditions typically resolve under chiropractic care as well. Headaches and dizziness (vertigo) are often caused by mechanical problems in the joints of the neck or upper back.
The other third of conditions chiropractors most commonly treat are of the shoulders (particularly rotator cuff injuries and adhesive capsulitis), hips (most often osteoarthritic problems), knees (both osteoarthritic and trauma-caused conditions), feet (plantar fasciitis for example), elbows, hands and jaw (typically clicking). In addition to back and peripheral joint pain, as well as headaches and dizziness (often referred to as neuromusculoskeletal [NMSK] conditions), some patients report (and there is scientific evidence for) improvements in certain pediatric and other non-NMSK conditions, such as fibromyalgia and PMS. Please contact the office for further information about possible treatment options for you.
Do I need a referral from my Medical Doctor to see a Chiropractor?
No. Similar to dentistry, chiropractic is a primary contact, portal of entry healthcare discipline. Patients can directly contact a chiropractor in order to schedule an appointment. Once examined by the chiropractor, the patient will be triaged and advised that their condition can be best managed by the chiropractor him or herself, co-managed (perhaps with massage therapy or some medical intervention) or referred to another, more appropriate health care provider.
What is a Spinal Adjustment?
A spinal adjustment, sometimes referred to as a spinal manipulation, is a directed high velocity (quick), low amplitude (gentle) thrust directed to a specific, targeted joint of the body. The intent is to restore a joint’s motion to its normal, optimal position in order for it to function properly. It is often accompanied by a popping sound, similar to when a person ‘cracks’ their knuckles. Typically a spinal adjustment is only delivered to a specific, targeted joint once per treatment, although a number of adjustments may be delivered to different joints during a treatment.
What is a Mobilization?
A mobilization is a low velocity, low amplitude oscillating therapeutic motion directed to a joint of the body, usually in a rhythmic manner. A mobilization is often used for joints that are arthritic, in an attempt to restore its full motion. It is also a very useful procedure to use after a trauma, such as a car accident or sports injury. If a joint is structurally weak (if it is osteoporotic for example) a chiropractor may chose a mobilization over an adjustment.
What is Myofascial Technique?
Myofascial technique is a type of soft tissue therapy that essentially takes a muscle from its ‘shortened’ position to its ‘lengthened’ position while the chiropractor firmly contacts a trigger point or nodule in the muscle itself. By doing so, an adhesions in the muscle can be broken up, allowing a muscle to return to its optional level of function. This type of therapy is very useful for chronic sore muscles in the neck-shoulder region, carpel tunnel syndrome, tendinopathies of the shoulder rotator cuff, tennis or golfer’s elbow, injuries to the hip flexors, injuries to the muscles surrounding the knee and plantar fasciitis.
Are Spinal Adjustments Safe?
Chiropractic therapy of all kinds has an excellent safety record. While not risk free, adverse reactions reported by patients typically include soreness as a result of the initial assessment and first few treatments. That said, many patients also experience immediate relief after their first adjustment.
More serious injuries are very, very rare. It is so rare, in fact, it is difficult to study. Estimates vary between 1 serious event every 100,000 treatments to 1 serious event to every 10 million treatments.
